Pond Plant ID
Your Complete Guide to Pond Weed & Algae Type Identification for Aquatic Vegetation Control & Management
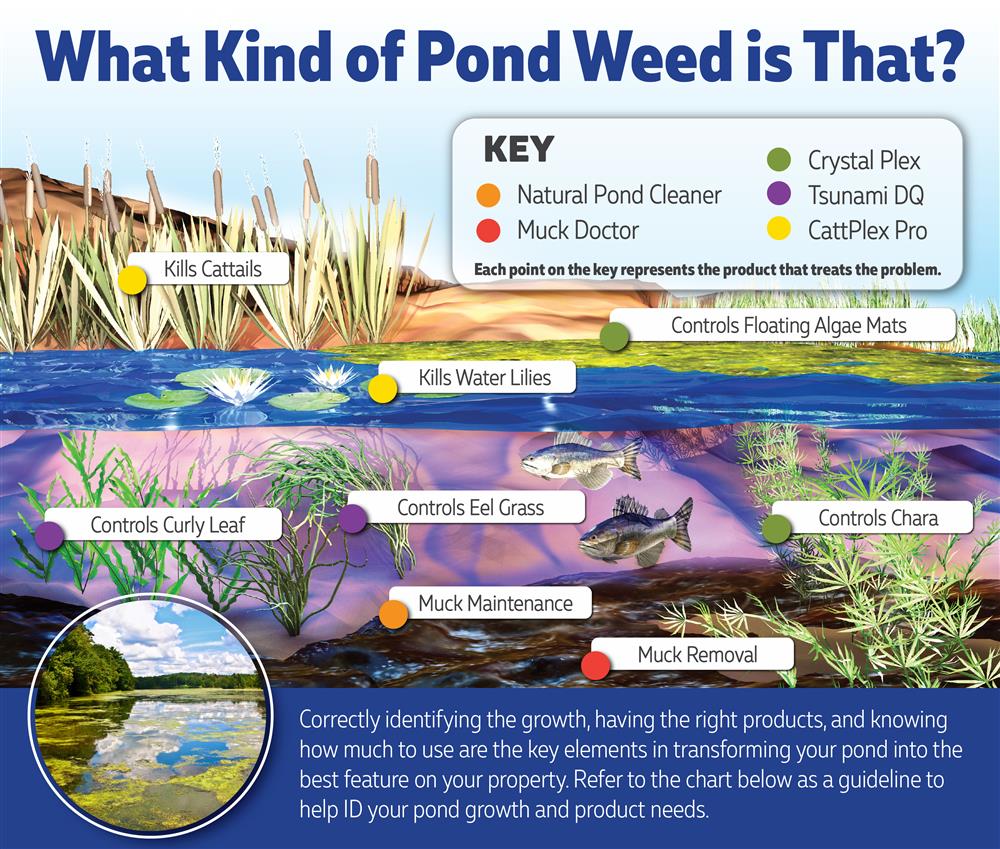
After finding out the size of your pond, the next step to treating your pond is to properly identify what you have growing. If you misidentify the growth you could be using/wasting a lot of money on pond chemicals that will give you no results. Pond weeds and algae are not the same type of growth therefore you will not use the same product to kill both. Some weeds can look like algae and some algae can look like weeds. Please refer to the images below to visually compare your growth with a picture. Let's start with Pondology. Solving Your Pond Problem. Note the key which matches a pond problem to a product that solves it.
Algae
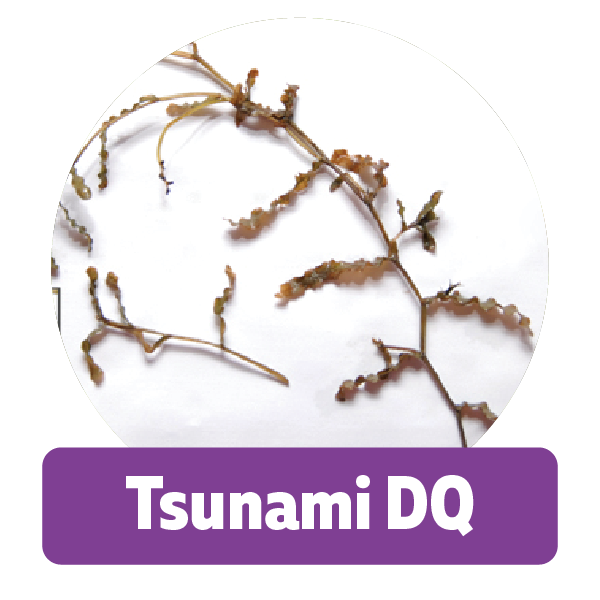
Green water, moss, hair like algae, scum, pond scum, slime, algae mats....All of these are names that are used to describe algae in ponds. There are many different forms of algae some are very easy to identify like filamentous algae, others, like chara are mistaken for weeds.
Filamentous Algae- Hair like algae that will be attached to the bottom of the pond floor and rocks. Filamentous algae will also break free and float on the surface in the form of thick algae mats.

Planktonic Algae- Microscopic algae that can turn your water pea soup green, brown, or even redish. They are such small organisms the only way you know you have them is when the water changes color.

Chara- Grows on the bottom of the pond floor in large pillows and is frequently misidentified as a weed. It will not grow above the surface of the water. Chara will also have a musky odor and a crunchy texture.

Oscillatoria- Is a form of filamentous algae that is sometimes refered to as black algae or blue-green algae. It can also give your pond a red-purple tint.

Submerged & Floating Weeds
There are hundreds of submerged and floating weeds that can grow in ponds and lakes. We have listed some of the most common weeds. Submerged weeds are best controlled with herbicides containing diquat. Submerged weeds are weeds that are rooted on the bottom of the pond and most of the plant if not the entire plant stays under water like coontail, bladderwort, and curly leaf pond weed. Floating weeds are plants that float on the surface of the pond or lake. The water will regularly wash over the top of the plant if the surface is disturbed at all like duckweed.
Large Leaf Pond Weed- Leaves both floating and submersed. Submersed leaves are large, oblong, wavy, and taper to the stem. Floating leaves are oval-shaped. Parallel leaf veins are evident. Stems are seldom branched. Leaves alternately arranged on stem. Solid, tightly packed spike of utlets at tip of weed rises above water surface.

Curly Leaf Pond Weed- Leaves thin with wavy and finely serrated edges. Stems branched. Upper leaves are often crispy and appear waxy. Leaves alternately on stem. Flowers born on spikes rise above the water surface.

Coontail- Leaves whorled around the stem and have a serrated appearance. Spacing between leaf whorls is variable. Consequently, weeds may be long and sparse or bushy. Near the end of the stem leaves and whorls are crowded. Branches are forked repeatedly. Do not confuse with Chara.

Duckweed- Leaves the size of a pencil eraser or a little smaller. May be observed individually or in clusters upon close observation. Small root hairs may be seen hanging down from the underside of the leaf. No stem is distinguishable. Heavy growth will blanket the surface with many inches of growth. Duckweed is not interconnected as is Filamentous Algae. Do not confuse with Algae.

Bladderwort- Finely divided leaves scattered along the stem with numerous bladder like structures on leaves. Stems have many branches and are densely leafy at the tips. Flowers are yellow and rise above surface.

Water Milfoil- Leaves whorled in groups of four. Each leaf is divided into many thread-like leaflets extending from a central rib. Forms tangled mats at the surface. Seed heads develop in mid to late season and may extend above the water surface. Treat when weeds are actively growing before flowering occurs.

Naiad- Plants of N. guadalupensis are rooted, submersed, and grow up to 3 feet long. The leaves are usually opposite, from 0.2 to 2.0 mm wide, and 0.1 to 1.5 inches long. The teeth along the leaf margin are small, 18 to 100 per side, and barely visible to the naked eye. Sheaths at the base of the leaf are rounded to slightly auriculate. The flowers are small, inconspicuous and borne in the leaf axils on the same plant.

Emerged Weeds
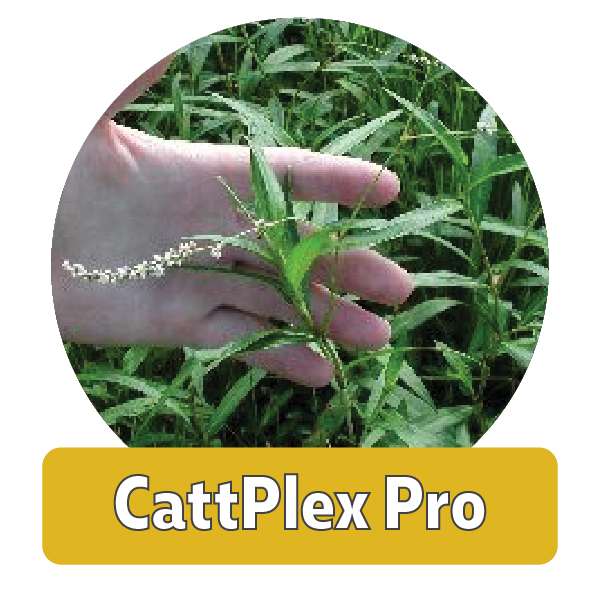
For plants that grow up out of the water you can use a Imazamox-based herbicide that will kill the plant to the root. Our CattPlex Pro is a Imazamox-based, Glyphosafe-free herbicide that is approved for aquatic use.
Water Lilies- Leaves large, round and slit to the center. Underside of leaf is often purplish. Stem is below the surface. Roots are thick and fleshy, most often buried in mud. Flowers have multiple rows of petals born on a single stalk at or above the surface. May be confused with Spatterdock.

Cattails- Leaves are tall and flat. Stems are tall, round and unbranched. Flower is the distinctive cigar-shaped cattail which is green in early summer and turns brown and fuzzy in fall. This weed has an extensive root system. Difficult to control when well established.

Bulrush- Leaves may or may not be present. If present, they appear as a continuation of the stem. Stems are tall and smooth and either round or triangular in shape. A loose cluster of brownish flowers and seeds is located near the tip of the stem.

Purple Loosestrife- Leaves slightly heart-shaped at base coming to a point at leaf tip. Leaves small and more numerous near tip. Stems rigid, four-sided and have fine hairs on them. Leaves oppositely arranged on stem usually in pairs. Flowers bright purplish on a spike closely attached to stem.

Reed Grass/Grass- Leaves are long and flat with parallel veins. Stems are tall and round with alternately arranged leaves. Flower of weed is made up of pikelets with long silky hairs such that this portion of the weed may appear as a silky mass. Stout rootstocks make this weed difficult to pull out.

Smartweed- Leaves are oblong and smooth on the edges. Stems are distinctly jointed with leaves alternately arranged. The lower portion of the stem is rooted at the joints. Flowers are small and tightly clustered and are white or pink in color. Weed may be mersed in shallow water or completely submersed with only flowers visible above surface in deep water.

Or view the Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants.
For more questions about Pond Plant Identification Contact Sanco.

